Nonwoven fabrics, scientifically known as nonwovens, are a novel type of textile material not produced through traditional weaving processes but by directly bonding fibers into a sheet-like material through mechanical, thermal, or chemical means.
The concept of nonwovens dates back to the early 20th century, but it was not until the 1950s that they began to be mass-produced and utilized with the advancement of industrial production technology.
Compared to traditional woven fabrics, the production process of nonwovens is simpler and faster, without the need for complex weaving or knitting processes.
Spunbonding is one of the most common methods in nonwoven production.
Meltblowing is a special spinning process that uses high-speed hot air to disperse molten polymer chips into ultra-fine fibers.
Hydroentanglement uses high-pressure water jets to mechanically work on a fiber web.
Needlepunching uses barbed needles to repeatedly puncture a fiber web.
Chemical bonding involves using chemical adhesives to bond a fiber web together to form nonwoven fabric.
As environmental awareness increases, the eco-friendliness of nonwoven production is becoming more important.
The strength and durability of nonwovens can be controlled by selecting different fiber types and adjusting production processes.
The breathability of nonwovens depends on the fineness of the fibers, the density of the fiber web, and the arrangement of the fibers.
The moisture absorption of nonwovens can be adjusted by the chemical properties and physical structure of the fibers.
The water resistance of nonwovens can be enhanced by applying waterproof agents on the surface or using special production processes.
Nonwovens can have improved stain resistance through surface treatments.
The chemical corrosion resistance of nonwovens depends on the type of fibers used.
The antimicrobial performance of nonwovens can be enhanced by adding antimicrobial agents or using antimicrobial fibers.
Nonwovens that are degradable can be produced using bio-based fibers or biodegradable polymers.
Nonwovens are widely used in the medical and healthcare fields.
Nonwovens are also widely used in household products.
The application of nonwovens in agriculture is mainly as covering materials.
Nonwovens have various applications in the industrial sector.
Nonwovens are used in the apparel industry as disposable protective clothing.
Nonwovens are used in environmental protection as soil erosion control materials.
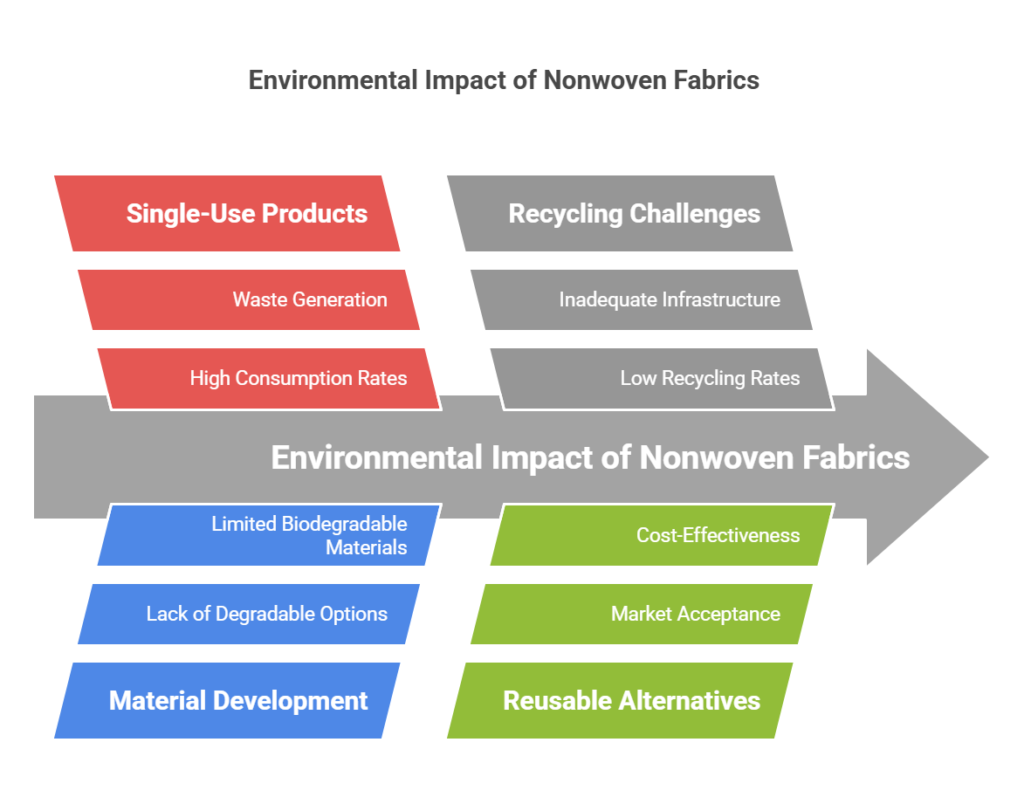
The widespread use of disposable nonwoven products has put pressure on the environment.
To reduce the environmental impact of nonwoven products, the development of degradable materials is key.
Establishing a recycling system for nonwoven products can reduce the demand for new raw materials.
Promoting reusable nonwoven products can reduce the consumption of disposable products.
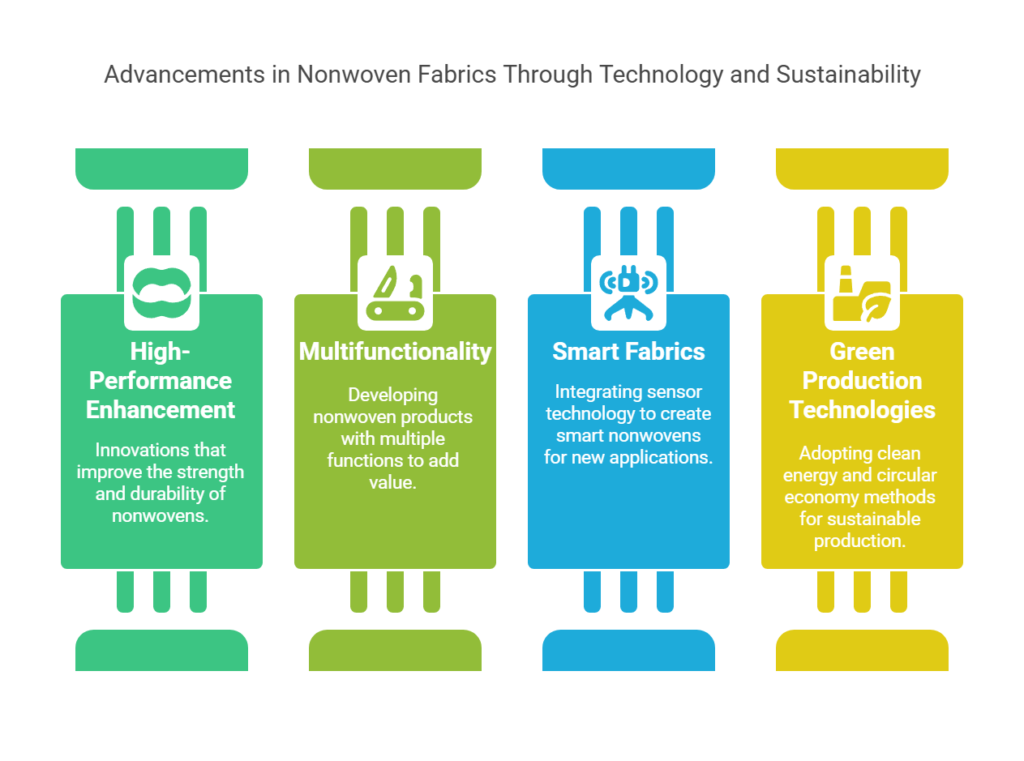
Technological innovations can improve the strength and durability of nonwovens.
Developing nonwoven products with multiple functions can increase the added value of nonwovens.
Combining sensor technology to develop smart nonwovens can open up new application fields.
Adopting clean energy and circular economy methods can achieve green production of nonwovens.
The market demand for nonwovens will continue to grow.
The nonwoven market is highly competitive.
The nonwoven market will show trends towards high performance, multifunctionality, and intelligence.
China is the world’s largest producer of nonwovens.
The international trade of nonwovens mainly flows to developed countries and emerging market countries.
Trade barriers and policies have a significant impact on the international trade of nonwovens.
Nonwoven fabrics have broad market prospects and development potential. They will continue to develop in the direction of high performance, multifunctionality, intelligence, and green production.